Tuesday 3rd November 2020
Media Industries and Audiences
L/O: To explore the content of unit
Paper 2 Section A:
- How and why media products are constructed
- To reach and address a number of audiences.
Disney
Ownership
Disney owns many companies such as ABC, ESPN, Touchstone Pictures, Marvel, Lucasfilm, A&E, The History Channel, Lifetime, Pixar, Hollywood Records, Vice Media, and Core Publishing.
Funding
ABC-Paramount put $500,000 equity, committed to take $2 million of ten-year intervals, and in addition guaranteed loan of $4.5 million – total of $7 million. In exchange, ABC-Paramount received a 34.48% of Disneyland.
Growth
From 1991 Disney’s gross revenue had a total of $6,111 million, and in 2019 the revenue peaked at $69,570 million.
Due to COVID-19; Disney saw a $6 billion drop in overall year-on-year revenue, from $20.25 billion to $11.8 billion.
Box Office Successes
At the end of 2019, Disney earnt 33% of all domestic box office grosses for the year which was the first time since 1999.
Frozen II was the highest grossing movie of all time with $1.32 billion which surpassed Frozen as the top animated film at the global box office.
Diversification
Disney has diversified by expanding from its core animation business into theme parks, live entertainment, cruise lines, resorts, planned residential communities, TV broadcasting, and retailing by buying or developing the strategic assets it needed along the way.
Influence and Brand Values
Values of Disney – “We create happiness b providing the best in entertainment for people of all ages everywhere”
Disney uses escapism as they emphasise you can “escape to a world of your imagination”.
The Jungle Book (1967)
Main Character:
Mowgli - protagonist
Bagheera
Baloo
Shere Khan
Kaa
Narrative(Todrov):
Equilibrium - Mowgli living with the wolves
Disruption - The wolves are told to return Mowgli to the village because Shere Khan will kill him.
Recognition - Lightning strikes a nearby tree and sets a fire, the vultures distract Shere Khan, while Mowgli grabs a large flaming branch and ties it to the tiger's tail. Shere Khan, being terrified of fire, runs away.
New Equilibrium - Bagheera and Baloo take Mowgli to the man village and Mowgli notices a girl getting water, she drops the pot and Mowgli retrieves it for her, and ends up following her into the village. Bagheera and Baloo are content that Mowgli is safe and happy, so they leave him be.
Themes:
Representations (groups, individuals, places, etc.):
Set in the jungle so the main characters (exception of Mowgli) are wild animals who tend to be in packs of their own kind such as the wolves and the vultures.
Tuesday 10th November 2020
The Jungle Book (2016)
Main Characters
Same as 1967
Narrative
Equilibrium - Mowgli happily living with the wolves
Disruption - Shere Khan threatens Mowgli because man-cubs turn into man (who gave him the scar) that means he wants him dead.
Recognition - Mowgli beats Shere Khan by fire.
New Equilibrium - Mowgli stays in the jungle with the animals.
Representation (groups, individuals, places, etc)
Groups - Pack of wolves represents being strong willed.
Individuals - Bagheera, Baloo, Mowgli
Places - Jungle and man village represents that "man" are dangerous.
What changes have been made?
Mowgli can climb trees
At the start of the movie, instead of Mowgli as a baby, it jumps right into the action of Mowgli in the jungle running from Bagheera.
All the animals join at the Peace Rock, including Shere Khan who has a vengeance on man who gave him a scar on his face. He threatens mowgli and says once the water from the Peace Rock evaporates, Shere Khan will return for Mowgli.
Instead of telling Mowgli to go, Mowgli himself says he'll leave to save lives of the pack, and willing goes off with Bagheera.
The elephants don't play as big of a part.
Shere Khan attacks Bagheera whilst taking Mowgli back to the man village and chases Mowgli.
Shere Khan goes back to the wolves and asks for Mowgli but as he has left out of spite Shere Khan throws the pack leads off the hills.
Unlike the 1967 version, Kaa is portrayed as a female and tells Mowgli his backstory and tells him about a Red Flower (referring to fire), which sets fire to the jungle and caused Shere Khan to have his backstory. Before consuming Mowgli, Bagheera bites Kaa.
Mowgli wakes up in a cave with Baloo, and Baloo says Mowgli needs to pay him back by climbing up a wall to get him honey. Mowgli makes a vine and whacks the beehive in which he gets being stung.
Baloo asks Mowgli to stay with him until hibernation, Mowgli says he can't stay, then Baloo says he'll take him there himself. Mowgli gives in and says he'll say until winter.
Shere Khan, the big meanie, says Mowgli will come back so he'll kill him.
Bagheera shows up, annoyed at Mowgli's tricks and says he's going back to the man village.
In the middle of the night Mowgli sneaks off to the elephants and helps the small elephant who was stuck down a hole.
After being told to go by Baloo; Mowgli climbs up a tree and sulks, A monkey comes along and makes fun at him and then a hoard of them carry him away, Bagheera and Baloo hear Mowgli's screams and follows him.
Bagheera and Baloo climb up the wall to King Louies palace in order to get to him.
Baloo walks into King Louie's temple and calls him fat. Bagheera sneakily goes in to rescue Mowgli. King Louie tells Mowgli that Akira has been killed by Shere Khan and proceeds to chase him. Mowgli jumps out of the temple into a tree, and King Louie gets crushed by his temple.
Mowgli, being angry at both Baloo and Bagheera, runs off and glazes his eyes on the red flow(fire) by the man village, and proceeds to take a touch of the flame throughout the jungle, accidentally setting afire.
Mowgli yells for Shere Khan and Shere Khan emerges sharing his predictions for Mowgli turning to man. Everyone chases after Shere Khan as they respect Mowgli and Bagheera tells Mowgli to not fight like a wolf, but like man.
Shere Khan finds Mowgli in a tree surrounded by fire trying to make a vine and tries to attack him. As Mowgli is inside the tree, it's difficult to get ahold of him. Emerging from the top of the tree, Shere Khan realises he's surrounded by fire and says he's either going to get killed by him or the red flower. The tree branch begins to break off, and as quick as a flash, Mowgli jumps onto the vine and swings away. Shere Khan tries to pounce but falls into the fire.
The elephants bring Mowgli back to the rest of the animals and create a dam to stop the fire being spread anymore.
After the incident, everything seems to be as it were as Bagheera is still teaching Mowgli, but this time he can do it his way.
How are advances in technology shown/used?
It shows the development of Disney from 1967 (being a cartoon) to 2016 with the live-action CGI effects of the movie, making it look realistic.
Tuesday 17th November 2020
The 1960s
L/O: To research the social context
The Jungle Book (1967 and 2016)
- You will be asked to make a comparative study of these two film texts.
- The question may be linked to productions, distribution, exhibition and/or consumption.
Specification:
- How the film industry has changed from 1967 to present day.
The Jungle Book (1967) is a historically significant media product. The 1967 film is current one of the most successful films of all time (taken over 100 billion US dollars) and followed a tradition pattern of production. Distribution and circulation, although it enjoyed a 'second life' on video and DVD.
The Jungle Book (2016) has taken over 1 billion US dollars already at the cinema box office alone (but will generate more income as a DVD/Blu-ray disc and online). The film has a clear pattern of production. Distribution and circulation that can be easily distinguished and is a film production from a major studio.
The 60s
- Acceptable in the 60s that's no longer tolerated now - attitudes to ethnicity, gender, smoking, drugs
- Unacceptable in the 60s but tolerated now - divorce, graphic representation of violence, etc
- Emerging post WW2 period, a decade in a vast socio-political revolution. Economies starting booming again in the 60s from the war, and was led by the youth culture.
- In the start of the 60s with music and fashion to the mid-60s of political actions such a protests and riots to challenge the old ways and fighting against wars such; as the second-wave of feminism, black civil rights and human rights.
Social/Historical Content
Key events from the 1960s
- First man in space
- First man to walk on the moon (1969)
- President JF Kennedy was assassinated
- Vietnam War
- Cold War
- The threat of nuclear war
- Collapse of the UK Commonwealth
-Strikes and unions
- Sexual scandals
Youth Cultures
- Mods and Rockers
- Beatles/Rolling Stones
- Hippies
- Drug culture
Equal Rights
- Legalisation of homosexuality
- Abolition of capital punishment in UK
- The Second Wave of Feminism (contraception pill)
Famous people from the 1960s
- Martin Luther King
- John F. Kennedy
- Malcolm X
- Nelson Mandela
- The Beatles
The Jungle Book In Context
How can the values, ideologies and key events of the 1960s be seen in The Jungle Book (1967)? What does a lack of some values suggest about Disney and its values?
Consider:
- Representation
Xenophobia - animals call Mowgli an outsider
"I'm the king of the swingers" - jazz music representing black culture to fight against slavery (associated with black ethnicity) King Louie intimate Louie Armstrong voice, reflecting the attitudes at the time meaning everyone is being racism, (shows subtle racism as monkey being black people).
Targets to parents/adults who take the kids to see the movies
Disney presents a conservative values in the movie (at the time it was acceptable)
Represents to modern pop culture
- Themes
Baloo - Represents the hippies (free love)
Girl at the end - The girl singing about collecting water from her family (housewife)
Mowgli - Goes to the girl which shows he chooses to go back to his own king
Vultures - The Beatles
- Narrative
How can the values, ideologies and key events of the 1960s be seen in The Jungle Book (1967)?
Key events of the 1960s are shown in the Jungle Book (1967) such as the examples of the modern pop culture of the time by the use of the song, "I'm the king of the swingers" from King Louie who is an orangutan represents Louie Armstrong (a jazz musician of the time). This key event shows the ideologies and values of the society at the time as black people are being represented as monkeys, this denotes to the audience as subtle hints of racism as jazz tended to be sung by black people to fight against slavey but has developed into pop culture and was widely popular at the time. This targets to the older demographic such as adults of parents who took their children to the cinema at the time (as that was the only way of seeing movies), as the older audience tends to be more conservative and dislikes the revolution of the younger audience who wants change. Also, the use of the four vultures in the movie portrays a British accent shows the pop culture of the Beatles as their music at the time was influential to the younger audience who are shown to be having an interest with the music.
What does a lack of some values suggest about Disney and its values?
Tuesday 24th November 2020
Disney
L/O: To explore the contexts of Disney in the 1960s
- Grossed over $100 billion to date ($4 million to make).
- Made by Disney Studios under Walt Disney Productions (Hollywood production company in animation studio)
- Animation studio responsible for developing the techniques of standard practices of traditional animation, developing the use of the multiplane to create an early 3-D like effect.
- The production of the film involved specialised techniques that are still part of Disney's brand identity.
- Due to its success, it was able to buy out companies such as Pixar and Marvel, to help improve their CGI techniques and use of digital technologies(buying out their competition).
- Disney Studios is seen as the leader of animation and art direction which has become a standard practices by the 1960s.
- It specialised animation process involve highly creative film makes using labour- intensive techniques from concept and production. (Jungle Book is a prime example of high-cost and top-quality animation).
Historical Context
- The Jungle Book is a landmark film(best written for Disney includes two Oscar-nominated songs.
- Soundtrack was the first to achieve gold disc status in the US for an animated feature film.
- The film credits a notable cast and production team that had been in place and worked together for a number of years.
Economic Contexts
- By the film was released, Disney already began diversifying into theme parks, tv series(coloured tv) and merchandising deals.
- Reaction to the 1950s baby boom (fall on cinema ticket sales in the 60s), increasing competition from TV. Younger generation were more involved with TV and new trends.
- Released in October 1967, grossed nearly $24 million then.
- Fourth highest grossing movie in 1967.
- Re-released in cinemas in the US in 1978, 1984 and 1990 (Disney refused to sell TV rights to their films, maintaining the 'classic' nature of their products).
- Many European screenings throughout the 1980s.
- Success shows how Hollywoods conquers all (home market and global).
- 1991 released as part of the Walt Disney Classic collection
- Limited edition DVD in 1999, 2007 platinum edition to celebrate the 40th edition.
- In 2010, the film was released as a Blu-ray/DVD/digital copy combo-pack
- By periodically reviving its assets, Disney gains longevity of sales. Captures the next generation who then commit to the brand loyalty.
- Released digital download via iTunes and available to stream on Amazon and Google. Now Disney Plus.
Ownership, distribution and control
- Making money out of just film is difficult
- Media companies practise vertical integration in order to maximise efficiency of the supply and distribution of the product
- The Jungly Book is an example of how important synergy and merchandise is to a media conglomerate as it commodifies a successful media text.
- Disney is the master of synergy - Merchandise in the 1930, theme parks in the 1950s, animated films of famous cartoon characters on ABC as advertisements for theme park. This strategy of cross-promotion has become a basis for the Walt Disney Company's rapid growth.
- Offer opportunities for both cross-promotional campaigns with other companies and for in-house cross-promotion marketing strategies. Exploting the popularity of its brand is a major profit source of Disney.
What were the differences between how Disney operated as a film studio and how other studios operated at the time?
Instead of having a storyline first, Disney focused on the characters before having an ending
Casted the voice actors, then designed the character around them
What was Walt Disney's own influence on the production?
The fact that the Sword in the stone didn't do too well.
He said the Jungle Book was too dark, and told his new animators not to read The Jungle Book.
Picked the casting of Baloo and Kaa
Where did the animators get their inspiration from?
Each other because of their friendship
How has Disney become and stayed one of The Big Six for so long?
Disney has become one of The Big Six by the use of their use of the specialised techniques in film and art shown in their films such as The Jungle Book which got two Oscar-nominated songs. Disney began diversifying their brand into theme parks, tv series and merchandise due to the fact their were less people going to the cinemas in the 1950s due to the baby boom. This meant there were less cinema ticket sales which were their main source of revenue, so creating tv shows and advertisements generates their brand a source of income just from in-home profit. This is has managed to generate both in-home and global profit through their theme parks and cinema revenue(tend to be visited by families) in which Disney became one of The Big Six brands.
Staying in The Big Six seemed to be relatively easy for Disney as they re-released their movies in cinemas for new generations who would then commit to the brand for their lifetime through the sense of nostalgia purposes. Disney also used synergy through its merchandise in the 1930s, theme parks in the 1950s, and then used their animated films as advertisements for their theme parks. This created cross-promotion globally as it increased the growth of Disney as a company.
How was The Jungle Book different in terms of production and technology at the Disney Studios?
The Jungle Book is different in terms of production by the way Disney operated as a film studio at the time. At the time of production there was no clear storyline as Disney wanted to focus of the characters before coming up with a new equilibrium for the story because he wanted to design and assign the characters around the actors to see who was the most suitable for the role. The characters were animated by a multiplane camera to make the cartoons feel real to the audience of children as they would feel a sense of connection through their use of storytelling. Disney popularised the technology of the multiplane camera, which became a a widely used technique to other animation studios.
Walt Disney himself had his own influence on the production of The Jungle Book due to the fact the previous movie (The Sword in the Stone) didn't do too well in terms of profit, so therefore he wanted him own influence to make a successful movie. To not make The Jungle Book too dark (which would diverge their family-friendly target audience), Disney told his new animators to not read The Jungle Book as the movie would only be based briefly from the book.
Tuesday 1st December 2020
The Film Industry
L/O: To explain the process of making a film and changes within the industry.
Film Making Process
What was the process of making films?
- The use of the quality of light in angles
- Scanning in film and making changes
How has it changed in the past 20 years?
- Digital cameras made it easier to film compared to before
- Use to be editing and cutting film
- First DI movie was in the year 2000
- Digital cameras could film in low-light in HD
- Made digital cameras (RED 2007) more affordable with higher quality (4K)
- Could do multiple things with the camera in terms of filming
What impact has digitalisation had of the industry?
- See exactly what you captured as you're filming
- Being able to talk to the actor whilst filming
- Shoot in a shorter amount of time
- Early digitalisation had a problem with resolution due to the lack of pixels
How has changing technology effect the industry?
- CCD chip (1960s)
- Sony produced its first CCD cam-recorder 1980s
- Shot on a digital camera video became cheaper (production aesthetic)
- Used floppy discs to store film (costly)
- Editing became easier
- From film being on black and white to the use of technicolour by the power of enhancement of colourists.
- DSLRs create still photography for their website but now can be shot for movies (cheap way for people to tell their stories/express themselves)
What's the future of filmmaking?
- CGI/digital cameras is becoming more realistic each year in film
- 5K cameras
- Delivery of the actors will change
- Savings in digital delivery and projections
- Digital projections itself is constantly improving
- Modern film and cinemas may be in danger in the future due to the fact there's so many ways to watch a movie though streaming platforms such as Netflix
- DSLR films may become more popular (so anyone can make a movie)
How can we see the impact of digitalisation and technical convergence in the production of the Jungle Book 2016?
We see the impact of digitalisation in the production of the Jungle Book 2016 by the use of the cutting edge CGI to create the animals to create a hybrid between live-action and CGI due to the fact the movie was filmed digitally compared it being on film in 1967.
We see the impact of technical convergence in the production of the Jungle Book 2016 by the fact there are various of choices on where to watch the movie (compared to 1967) such as at home through online streaming services (Disney Plus), DVDs, and also the cinema. This creates a sense of escapism to the audience when they watch the movie, and the fact they have multiple of options shows they can enjoy the movie at the comfort of their home without having to worry to go out.
Tuesday 8th December 2020
Jungle Book 2016
L/O: To explore the production and distribution of the Jungle Book 2016.
Vertical and horizontal integration
- Vertical integration is a strategy where a company owns or controls different businesses in the same chain of production and distribution. It benefits companies by allowing them to control process, reduce costs and improve efficiencies. Same industries.
- Horizontal integration is the process of a company increasing production of goods by buying up competitors in the same section of the market. It can lead to monopoly if a company captures the vast majority of the market for that product or service. Different industries.
Convergence (digital, technical and standard)
- Standard Convergence: of media occurs when multiple products come together to form one product with the advantages of all of them.
- Technical Convergence: The growing interaction use of digital technology in the film industry and media which enables people to share, consume and produce media that was difficult of impossible just a few years earlier. E.g. Pirate downloads, digital production.
Pre-production, production, distribution, exhibition, exchange.
- Stages to making a film
Jungle Book 2016
Director of the Jungle Book
Jon Favreau
Production company of the Jungle Book
Walt Disney Pictures
Director's previous two big CGI based successes as a producer?
Iron Man and Iron Man 2
Main difference to the original film?
2016 - Darker theme and atmosphere
Production
Estimated production budget - $175 million
- Above-the-line costs(creative talents, actors, directors, producers, etc)
- Below-the-line-costs(crew, technical equipment hire, sets, etc)
- Marketing budget
- Two flops in 2012 and 2012, so it made sense to remake a movie with a proven business track second and secure audience.
- Disney gave Favreau room to experiment as they wanted to create a visual spectacle that could easily translate across global markets.
- It can be describes as a live action/CGI fill as it combines the two on screen. CGI created by British company called MPC.
- The animal characters wee deliberately created with a realistic look, to target to older movie-goers.
- The production process of Jungle Book 2016 easily highly dependent on other companies such as MPC, so was not filly made in house, as Jungle Book had been (horizontally integration).
- Walt Disney chairman one of the series of remakes of classical properties. Revive characters for a new generation of kids, and parents.
- The proliferation (rapid increase in the number or amount of something) of of digital technology in film had been driving film production providing the most fantastical features.
Genres that help the most - Action, fantasy, sci-fi, etc...
Examples of films from 2010-2015 that show this?
Alice in Wonderland, Transformers, Guardians of the Galaxy, etc...
- Disney wanted to create an "immersive experience", creating a difference between the live action and animation. Disney is a business model which sees the potential for media synergy and cross-media products.
- Reduces risks and offers the potential to maximise the profit to create non-film revenue streams such as merchandise.
- By working alongside media companies the synergistic benefits of cross-promotion are effectively doubled. Disney is able to strike deals to make films and spin-offs.
- Disney chose to use of it subsidiaries to distribute the film - meaning no costs. They granted licenses to other companies to provides related merchandise.
Distribution
- The 2016 film was distributed by Walt Disney Studios Motion Pictures. handled theatrical release, marketing and promotion of films produced globally.
- released from April - July 2016 in 70 countries, opening at different times depending on competition and targeted school holidays dates.
- Produced in 3D and was the first film, to be released in Dolby Vision 3D
- JB16 estimated $175 million to produce by opening with $103.6 million in North American, making it one of the biggest April debuts ever at the box office. Grossed $966 million fifth highest grossing film of 2016 and 35th highest film of all time
- In 2016, Disney amassed $2.56 billion globally well ahead of rivals.
- Released on DVD and Blu Ray, digital download, and now streaming.
- The current trend for making theatrical release windows shorter between different countries in fuelled by the growing importance of non-theatrical revenue sources.
- At present, DVD sales account for almost twice the profit earned by theatrical exhibition
- Cinema has been the source of the highest revenue in the shortest, cascading down through home exhibition, TV and so on.
Explain how the production and distribution of major Hollywood films have changed since the 1960s. Refer to the two version of The Jungle Book to support you answer.
In your answer, explain how historical and economic contexts influence this.
The production of major Hollywood films have changed since the 1960s by the use of Walt Disney Pictures (2016) and The Walt Disney Company and Walt Disney Animation Studios (1967). Compared to the 1960s version, the 2016 remake has more development for distribution by the use of the various types of technical convergence such as online streaming services(Disney Plus), cinema, and digital download. This meant that Walt Disney Pictures could generate more profit by the use of vertical integration of their movies, but also the use of horizontal integration from Disney as a company itself by the fact it uses
Tuesday 15th December 2020
Disney 2016
L/O: To explore the marketing techniques used in 2016
Distribution Agreements
- Film distributions are involved with film before productions, advising on its marketability
- Distribution Agreements Cover: the promotion in all media before and after release, different cuts necessary for different cultures or territories, how the income for its release would be apportioned, how far the distribution licence extends into other markets such as TV and home entertainment
- The objective is to create 'visibility' for an individual film and engage to the audience's interest
- The proliferation of films, interest needs to be built to a peak just before the film opens at cinemas.
- Early release windows can create issues with substitutability but then benefit from the buss it creates. This is why theatrical release are but less profitable than subsequence release formats - this was not the case with The Jungle Book 2016.
substitutability - When a film is shown in cinemas and then made available on DVD, etc.
Promotion
- word-of-mouth (such as social media)
- Posters
- Trailers
- Social media
What did Disney do to promote and advertise the release of the Jungle Book 2016?
- Jon Favreau bounded onto a 7,800-seat arena and showed sneak-peek footage of his film.
- Disney promoted an action-oriented trailer during the Super Bowl
- Disney teamed with Univision for a five-week stunt that brought Jungle Book characters and clips to telenovelas, talk shows and sports coverage.
- Learned that Hispanic moviegoers tend to buy tickets in large groups such as family members, so Disney reached out in Spanish.
- Disney introduced a maze-like 'law of the Jungle' website.
- Disney empire pitched in to promote "The Jungle Book" on New Year's day on the Disney channel to portray the film as one of the year's first blockbuster offerings for families and children.
- During Spring break, they released sneak-peek footage of the movie in park theatres in Florida and California.
- Park stores that sell Disney merchandise had "Jungle Book" sections.
- Created a VR experience
- Released the voice actors to target to parents
- Disney uploaded an interactive Snapchat filter of Kaa.
IMC Campaign of the month - The Jungle Book
- Disney pitched the Jungle Book to male audiences
- Made an extended 3D trailer fro the Jungle Book which was played during the showing of Star Wars: The Force Awakens, which the audience was majority male.
- Wants to show off their new technology by the use of CGI
- Special promotions at IMAX cinemas
- Initial trailer, teased 7 second clip on Instagram
Explain how the marketing of major Hollywood films has changed since the 1960s. Refer to the two version of the Jungle Book to support your answer.
Hollywood films such as the Jungle Book 1967 had marketing only in cinema trailers as that was the main way the audience would know that there's a new film coming out at the time. Comparing it to the Jungle Book 2016, marketing itself as changed considerably due to the fact of the increase of technology, and the decrease of people going to the cinema to see the trailers.
New Hollywood movies would be a big event in the 1960s, and since Disney itself created a sense of nostalgia with its target audience, it would also be a big event. As new Hollywood movies would always be shown only at cinemas, people of interest would go and watch the movie, and since Disney's net worth is so massive (even in the 60s due to their cross-promotional advertising), Disney would pay for their trailers to be shown at all upper coming movies, which would then create a word-of-mouth promotion for their films, but also the use of merchandise and the us of theme parks. The Jungle Book 1967 got its recognition by the use of their theme parks to create specific merchandise and set the park around the Jungle Book to attract the audience to the film. Also the fact that Disney used long-profit method of releasing their movies by re-releasing them every ten years again in cinemas to attract the old audience. This would target to the adult audience who have a sense of nostalgia with Disney already, that would want their children to have the same feeling they had when they were a child.
Similarly to the 1960s, modern day Hollywood movies also use marketing of posters, word-of-mouth and trailers, but now it's targeted to a more mass of audience's by the use of trailers not just at cinemas, but also on YouTube and other platforms of Social Media so anyone everywhere can have access to the release of the trailer. Disney markets the Jungle book 2016 by using social media to promote their CGI filter on Snapchat to adapt the audience of young-adult/teen audience in todays adaptation which would make the audience immerse themselves with the film, making the audience intrigued, wanting them to watch the movie.
(20 mins)
IMPROVEMENTS
Friday 8th January 2021
Analysis Structure
L/O: To refine analysis and exam technique
Explain how the production and distribution of major Hollywood films have changed since the 1960s. Refer to the two version of The Jungle Book to support you answer.
In your answer, explain how historical and economic contexts influence this.
The production of major Hollywood films has changed since the 1960s by the use of Disney's both horizontal and vertical integration shown through theme parks, and Disney itself buying out competitions such as Pixar. The improvement of technology from the 1960s has also impacts major Hollywood films as CGI from 2016 Jungle Book looks realistic, and the fact that Disney expanded their target audience to teens by the use of marketing through Snapchat filters means it won't just target to teens, but to teens throughout the world.
Compared to the 1960s version, the 2016 remake has more development for distribution by the use of the various types of technical convergence such as online streaming services(Disney Plus), cinema, and digital download. This meant that Walt Disney Pictures could generate more profit by the use of vertical integration of their movies, but also the use of horizontal integration by the fact that Disney has bought out its competition such as Pixar and 21st Century Fox so they can be the world's major media conglomerate.
Tuesday 12th January 2021
Disney Audience
L/O: To analyse the target audience for Disney.
Who were Disney's target audience in the 60s?
- Family
1960s Target Market
- Disney's primary target market of 4 - 12 year old boy and girls has been unchanging for decades.
- It is widely diverse as it includes both the very young and those that are nearly teens.
-These two segments are considered primary because the have the greatest influence over their parents' decision making and are most excited about the brand.
- They are also heavy users of the brand in terms of merchandise and as a source of entertainment.
Audience
- The secondary target audience is therefore (parent 35 - 55) as they are the money makers and make Disney experience available to their children. Much of the appeal to them is based on nostalgia.
- Both the primary and secondary target markets are very trusting of the Disney brand due to its longevity and the association with customer service and quality.
- In 1967, the brand offered a wide array of products (TV shows, movies, theme parks, toys, etc) that satisfied both segments needs and desires.
- Children felt a strong association with many characters; parents were confidents in the wholesome values of the brand in a shifting society context.
How can we see that the 1967 film was aimed primarily at a family audience?
- The narrative is based on the Jungle Book book released in 1894, so parents may have read the book as a child.
- The characters were based off the appearance of the voice actors in the film, parents would have a sense of familiarity from other films.
- The songs from the soundtrack are upbeat and catchy so children would like it, but for the parents it would be the orangutan (King Louie) portray the musician Louie Armstrong.
Who are Disney's target audience now?
Disney have broadened their target audience to compete with other studios.
2016 Target Market
- The 2016 film succeeded in attracting a wide range of age groups - not just the under 12s or traditional family audience to see the film.
- The success is largely due to the brand's ability to market and distribute the product and to value its audience.
- The 2016 film reinterpreted the characters and narrative for a more modern age and the new technology appealed to technophiles everywhere.
- The more adult themes, the darker the atmospheres, the actions credentials of the studio and director and the other action conventions followed appealed far more to a predominantly male audience.
- The subtle hints to the original maintained the sense of nostalgia and humour for older generations.
Success
- Moreover, Disney adapted to the online age with the use of social networking to promote the film triggering even more audience engagement and interaction with its marketing strategies, This reflects the modern age of film marketing which is dominated by CGIO and visual effects technology.
- This effective utilisation of the company's massive resources and power created an immersive viral campaign that was consumable by all age ranges when allied with traditional marketing strategies.
- The JB2016 made over $966million globally; it won the Academy Award for Best Visual Effects. It enjoyed unrivalled success globally. Disney successfully created a fan culture for a movie, for a whole new audience, all over again.
How can we see that the 2016 film was aimed at a more broader audience?
The fact that Disney appealed the 2016 Jungle Book to a male audience by the use of darker themes such as Mowgli, a male, setting fire to the whole jungle.
Disney now - What's difficult about analysing the social context of the present?
The traditional family audience has changed as the movie was pitched to a much wider youth audience than the 6-12 year old in the 1967 version.
2016 was the year of Trump and Brexit; Syrian boat refugees; ongoing oscarssowhite campaign; the Ferguson riots of 2014.
Research Time
- Research the key events as issues going on here and in the US during 2014-2016
Politics
US 2014 - Barack Obama in his second term.
US 2016 - Donald Trump defeated Hilary Clinton in the presidential election.
UK 2014 - David Cameron was PM.
UK 2016 - Theresa May became PM.
Key figures
US 2014 - Robin Williams(died).
US 2016 - Hilary Clinton, Bernie Sanders, Donald Trump.
UK 2014 - Emma Watson UN speech
UK 2016 - David Bowie(died)
Social media storms
US 2014 - Snapchat having the fastest growth. 71% adults use Facebook.
US 2016 - 79% adult use Facebook.
UK 2014 - 70% of the population use social media.
UK 2016 - 87% of the population use social media.
Key events
US 2014 - Ebola Epidemic became a global health crisis (two cases in the US)
US 2016 - Russia interferes with presidential election(Donal Trumps with election).
UK 2014 - Voters in a referendum in Scotland reject independence.
UK 2016 - Britain votes to leave the EU.
How can you link these to the narrative or the appeal of the 2016 Jungle Book?
The use of escapism from real-life problems.
Inclusive society
Friday 15th January 2021
Minecraft (2011)
L/O: To explore Minecraft and the history of gaming.
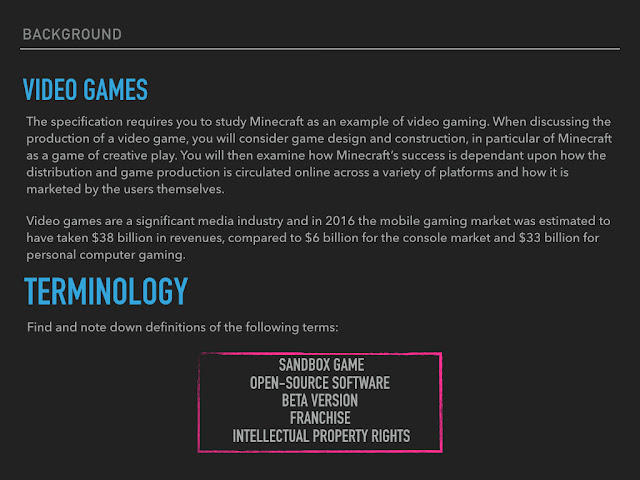
Sandbox Game - A video game with a gameplay element that gives the player creativity to complete tasks towards a goal within the game.
Open-source Software - A type of computer software in which source code is released under a license in which the copyright holder grants users the right to use and distribute the software to anyone and for any purpose.
Beta Version - A version of a piece of software that is made available for testing, typically by a limited number of users outside the company that is developing it before general release.
Franchise - A right to sell a company's products in a particular area sung the company's name.
Intellectual Property Rights - Are the rights given to a persons over the creations of their mind.
What does this cover tell us about the game?
This cover suggests to the audience that the game is going to be about mining with animals which could aim at a younger target audience by the use of its bright colours.
More people game than ever, 40% said that gaming improves emotional well-being.
What are the different types of games you can get and how do they differ?
Action - Emphasises physical challenges including hand-eye coordination and reaction-time. (GTA)
Adventure - Plays a fantasy role in an episodic adventure story. (The Legend of Zelda)
Action-adventure - Combines elements of adventure with action. (The Legend of Zelda)
Role-playing - Player can be an imaginary character and behave like them. (Final Fantasy VII)
Simulations - Simulates real world activities. (Flight simulation)
Strategy - Enables the players skilful thinking and planning. (Warcraft)
Sport - Simulates the practice of sports. (FIFA)
Puzzle - Solving puzzles to test the players problem-solving skills. (Undertale)
Horror - Centred on horror fiction to scare the player. (Resident Evil)
Massively multiplayer online - Also knows as MMO, which is online games with a large number of players. (SoulWorker)
Otome - Aimed at girls. (Mystic Messenger)
Sandbox/open world - A world the player can do whatever they want. (Minecraft)
Which are the main game companies?
Consoles - Nintendo Switch, PlayStation and Xbox.
Game producers - Nintendo, Sony, Microsoft.
Find some recent statistics about audience demographics.
When was Minecraft released, who designed it and which company produced it?
18th November 2011 - Mojang Studios.
What is the idea of the Minecraft?
Survival mode - Players are challenged to survive.
Creative mode - Access to any and everything so players can explore their creativity.
Who was the target audience?
5-15 year old males.
How has Minecraft developed?
Created by Markus Persson in Java in 2009, in 2011 Jens Bergensten took over the development.
Who owns Minecraft it now?
Microsoft.
Tuesday 19th January 2021
Minecraft
L/O: TO explore the game feature and initial development.
The World of Minecraft:
- Every time you start a new world in Minecraft, it's unique. Levels are randomly generated based on a set of parameters.
Constants:
- The levels always contain the same materials.
- There is a day/night cycle.
- At night, enemies appear and will attack you.
- You can only dig so deep below the world's surface before hitting bedrock.
- The world that spawns always has stiff to discover, whether it's crazy jungle or mountains o underground caves.
There's a creation mode that enables exactly that with no day/night cycle, no enemies, no mining if you don't want to. Just endless creation.
Genre and Format
- Minecraft is a sandbox/open world game with its key focus on building and survival.
Modding and Extensions
- Minecraft is available for most platforms.
- Has thousands of mods.
- Some mods have allowed players to add brand new items and gameplay dynamics to the fame while other have allowed multiplayer Minecraft world o have their own meaningful economy.
- Mojang provided an almost endless supply of extension strategies for when players get bored of the core gameplay.
- This is a valuable trait to have in a game, especially when it powers an ability to manipulate what the game offer into something more useful.
Minecraft is a form of 'Artistic Expression'.
- I agree with the statement because in creative mode you are free to create whatever you want, whenever you want, such as infinite types blocks, meaning the player has so much freedom in creating whatever they want.
Initial Development
- Persson inspired by the game Infiniminer; an open source software and multi-player-based sandbox building and digging game. Was heavily influenced the style of gameplay, visual style and building fundamentals.
- Persson is an independent producer developing a game concept outside mainstream media.
- Minecraft sprang from fantasy RPG. Persson enabled was the development within the game of a role from a first-person perspective in a creative and imaginary way. His vision was made possible by allowing players to develop an identity through gameplay.
- Persson being an independent producer wanted the game kept for 'gamers' and as he developed the concept he tried to resist the temptation of large multinational companies. This is demonstrated when whole studios receive either praise or criticism for a new game, rather than an individual.
- Minecraft is the story of opportunities available to an independent games producer on the digital age.
- Without the commercial backing of a mainstream publisher, no money spent on advertising revenue, the game relied on word of mouth between gamers and featured on sites such as Penny Arcade web comic to generate the interest amongst gamers. This wouldn't have enabled growth for companies. But in the online age, Persson had the vision to circulate and generate the game via the internet and the gaming community, so spreading the message virally. By January 2011, the beta-version of the game had passed over one million purchases om just one month, and by April 2011 Persson estimated US$33 million of revenue had been made.
- November 2011 , Minecraft has over 16 million registered users and 4 million purchases. Minecraft was released across multiple platforms becoming a commercially viable franchise with increased interactivity. In particular; Minecraft: Pocket Edition was released on Sony Xperia Play, available on Sony Xperia smartphones. Minecraft also became available on Android and iOS devices shortly after.
- Franchise deal with Sony to distribute the game that was a key feature of its success. This commercial deal helped secure Minecraft's place in the video game market. It was packaged as a game brand for a wider global audience and not jus gamers; the rapid rise in sales and popularity was a result of having identified markets among both existing gamers and newer phone-savvy digital players.
Persson wanted to spread Minecraft's concept and ethos within the control of genuine gamers. He also understood, however, that the game's success would grow with the backing of the technology companies, as they could provide him with multiple digital platforms to distribute the game - ultimately to reach all the non-gamers now using mobile devices.
Which developments in gaming do you think have transformed gaming technology and influence the development of Minecraft?
The developments in gaming such as the improvement of game consoles and mobile phones have transformed gaming technology as people can game from home easily, meaning game companies have been able to experiment with new genres of games. This influences the development of Minecraft as Persson was able to work on Minecraft without being in a company, which meant he could use inspiration from other games, integrating the hyriid of genres used in Minecraft. As mobile phones became more digitally powerful, such as Sony Xperia, it would be able to run games such as Minecraft: Pocket Edition which also increased the amount of mobile phone gaming.
Explain how the production and initial development of Minecraft is an example of a concept developed among a game community independently of the video game industry.
As Persson was the independent producer for Minecraft, the production of the game was much lower than large multinational companies, so Mojang Studios had no commercial backing which meant no money to spend on advertisement on Minecraft. But as the game was featured on Penny Arcade web comic it would targeted to the individuals most likely to play the game, which was then be spread through word-of-mouth through the internet and gaming community. This wouldn't of worked for many other media companies as it wouldn't of enabled growth of the game, but with the online age, Persson had managed to spread the message of his Minecraft virally.
Friday 22nd January 2021
Minecraft (2011)
L/O: To explore the distribution and takeover of Minecraft.
Distribution
- The development of Minecraft in 2011 occurred at the time when gaming went 'online' and was characterised by multi-gaming platforms. This was in part a response to gaming not just for consoles but any device.
- This opened up the opportunities for games distributers to connect to wider non-traditional gamers to game on media devices like phones and tablets. As well as digital distribution allowed easy access to global markets - Persson and Sony took full advantage of this.
- It was at this point that Minecraft became a media product that could be packaged and distributed across multiple platforms to offer its users and education value, and with apparently limitless boundaries to its gaming.
What are the advantages of distributing cross-media content?
Establish long-term relationships with the audience as content will be on multiple platforms such as consoles, phone and PC.
Research and create a timeline of the progress of Minecraft's global success from 2011-now.
2011 -
Availability on different consoles: Xbox 360.
Copies sold: 4 million.
Takeover: $33 million
Popularity: 16 million players.
2012 -
Availability on different consoles: Xbox 360.
Copies sold: 15 million
Takeover: $101 million
Popularity: 6th best-selling PC game of all time.
2013 -
Availability on different consoles: Xbox 360, PS3
Copies sold: 13 million.
Takeover: $130 million.
Popularity:
2014 -
Availability on different consoles: Xbox 360, PS3, Xbox One, PS4, PS Vita.
Copies sold: 60 million.
Takeover: $165 million.
Popularity: Best selling PC and console game of all time.
2015 -
Availability on different consoles: Xbox 360, PS3, Windows 10 Edition, Pocket Edition, Xbox One, PS4, PS Vita.
Copies sold: 70 million.
Takeover: $350 million.
Popularity:
2016 -
Availability on different consoles: Xbox 360, PS3, Windows 10 Edition, Java Edition(PC/Mac), Pocket Edition, Xbox One, Wii U.
Copies sold: 100 million.
Takeover: $420 million.
Popularity: 40 million players.
2017 -
Availability on different consoles: Xbox 360, PS3, Windows 10 Edition, Java Edition(PC/Mac), Pocket Edition, Xbox One, Wii U, Nintendo Switch, PS4, PS Vita.
Copies sold: 122 million.
Takeover: $370 million.
Popularity: 55 million players.
2018 -
Availability on different consoles: Xbox 360, PS3, Windows 10 Edition, Java Edition(PC/Mac), Pocket Edition, Xbox One, Wii U, Nintendo Switch, PS4, PS Vita.
Copies sold: 154 million.
Takeover: $500 million.
Popularity: 74 million players.
2019 -
Availability on different consoles: Xbox 360, PS3, Windows 10 Edition, Java Edition(PC/Mac), Pocket Edition, Xbox One, Wii U, Nintendo Switch, PS4, PS Vita.
Copies sold: 190 million.
Takeover: $375 million.
Popularity: 91 million players
2020 -
Availability on different consoles: Xbox 360, PS3, Windows 10 Edition, Java Edition(PC/Mac), Pocket Edition, Xbox One, Wii U, Nintendo Switch, PS4, PS Vita.
Copies sold: 200 million.
Takeover: $415 million.
Popularity: 126 million players.
Microsoft Takeover
- Minecraft wanted to make an official marketplace for Minecraft creations(sell their work directly to players).
Date of broadcast
- 2nd March 2021
Special features and key talking points
- Embarrassing stories about neighbours watching you
- 9AM = 10 minute takeover
- Teen first dates
- Unpopular opinions
- Celebrities going into politics
Hosts, guests and interviews
- Greg James (host)
- Nick Grimshaw (guest)
- Interviews the audience about their experience (example, watching neighbours, game)
News Stories - How many are "serious" and how many are "celebrity" news stories?
- Vaccines(how affective they might be) - serious
- Football (celebrity)
- Northern Ireland out of lockdown (serious)
- Duke of Edinburgh moving hospitals (celebrity)
- Taylor Swift "degrading women" (celebrity)
- Instagram blocks millions of fake accounts a day (serious)
8AM News -
- Vaccines
- Student asks university for £5,000 for lost work because of lockdown
- More football (2030 world cup Boris Johnson put £2.8 million towards it)
- Someone banned for putting dead horse on social media.
- Weather
8:30AM News -
- PM offering to host premier league in the UK
- Affective of COVID vaccine (over 80 badly ill)
- Brazil variant
- Football again
- Tennis Andy Murray
9:30 News -
- UK couple host all summer European championships(COVID concerns)
- More evidence of Brazil variant
- Student asks university for £5,000 for lost work because of lockdown, other claims were rejected
- Love Island in South Africa needs more diversity
- Weather (cold and cloudy)
Examples of how the show "Informs, educated and entertains"
- Inform = News
- Educate = Good hygiene is important to reduce the risk of Coronavirus
- Entertain = The host is charismatic
Examples of how the show being challenging, original, innovative and nurturing UK talent.
- Promoting upper coming UK artists (Wolf Alice)
- Calling the British audience to ask them about their experiences (e.g. questions)
- Audience tell about their findings
Key ways the show targets its audience?
- A lot of celebrity news to keep the younger audience engaged
- Music that'll appeal to the target audience (new music)
Fun Stuff: games, quizzes, etc.
- Quiz: Random questions
- Game: Top of the shops (guessing game)
- Reads audiences comments
- Unpopular opinions: asking the audience to give their unpopular opinions to be on the show
Relevant quotes
-
Tuesday 4th May 2021
L/O: To explore the exam format.
Media Industries and Audiences.
Question 1 - Contexts
Jungle Book:
Minecraft:
Question 2 - Knowledge and understanding question (Jungle Book and Minecraft)


















This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteGreat notes Kylie, well done!
ReplyDeleteDISNEY RESEARCH:
Great notes with some really useful facts!
1967 VALUES ANALYSIS:
Good ideas - don't be afraid to write about racist issues. No one is suggesting these are your views. I think the main point here is that, at the time, certain levels of racism were acceptable and normal for the mainstream conservative older generation.
24/11 (60s Context): great notes and a strong analysis!
ReplyDelete01/12 (Side by Side notes) Good - well done.
08/12 (JB16 P&D): Good notes
ReplyDeleteHOMEWORK: A good start but nowhere near enough!
15/12 (JB16 Marketing): Good notes. Exam practice - a good start but you will need to get faster at this. Good work on the 60s context - more needed on the modern comparison.
JB Marketing DIRT: better Kylie! Well done. I still think a bit more detail overall would help, but you're including more of the context.
ReplyDelete(Can you make your pink a bit more pink??)
08/1/21 Exam Practice
ReplyDeleteA good start Kylie
WWW: you show some knowledge and understanding of the production and distribution process in film and how it's changed over the years.
EBI: you need specific, detailed examples from both case studies and more details on the changes and context.
12/01/21 JB Audience
ReplyDeleteGreat notes and linking of the texts to the changing audiences. Your research is strong - just need to consider the more the contextual links other than escapism.
15/01/21 (Minecraft Research)
ReplyDeleteGood research and insight into the changes in the gaming industry. Well done!
19/01/21 (Minecraft Production)
Brief answers. Don't forget the role of allowing the gamers develop the game.
22/01/21 (Minecraft takeover)
ReplyDeleteGreat research and responses to tasks.
26/01/21 (Minecraft takeover impact)
Again, good responses but some areas are too brief (education) - this shows in your exam answer. the first half if much stronger with accurate details and explanations. The second half lacks the details.
02/02/21 (MC Marketing)
ReplyDeleteGreat notes.
05/02/21 (MC Audience)
Good notes - just add in how the game's ethos and design reflects the mainly male audience.
09/02/21 (MC Essay Qs)
ReplyDeleteExcellent Kylie! Detailed and accurate.
DIRT: fantastic response and additions. Spot on!
26/02/21 (BBC Research)
ReplyDeleteGreat notes and research on the BBC
02/03/21 (Episode notes)
Fantastic notes Kylie - loads to use there.
DIRT: don't forget to mention the genre and examples of music/artists played - part of the remit.